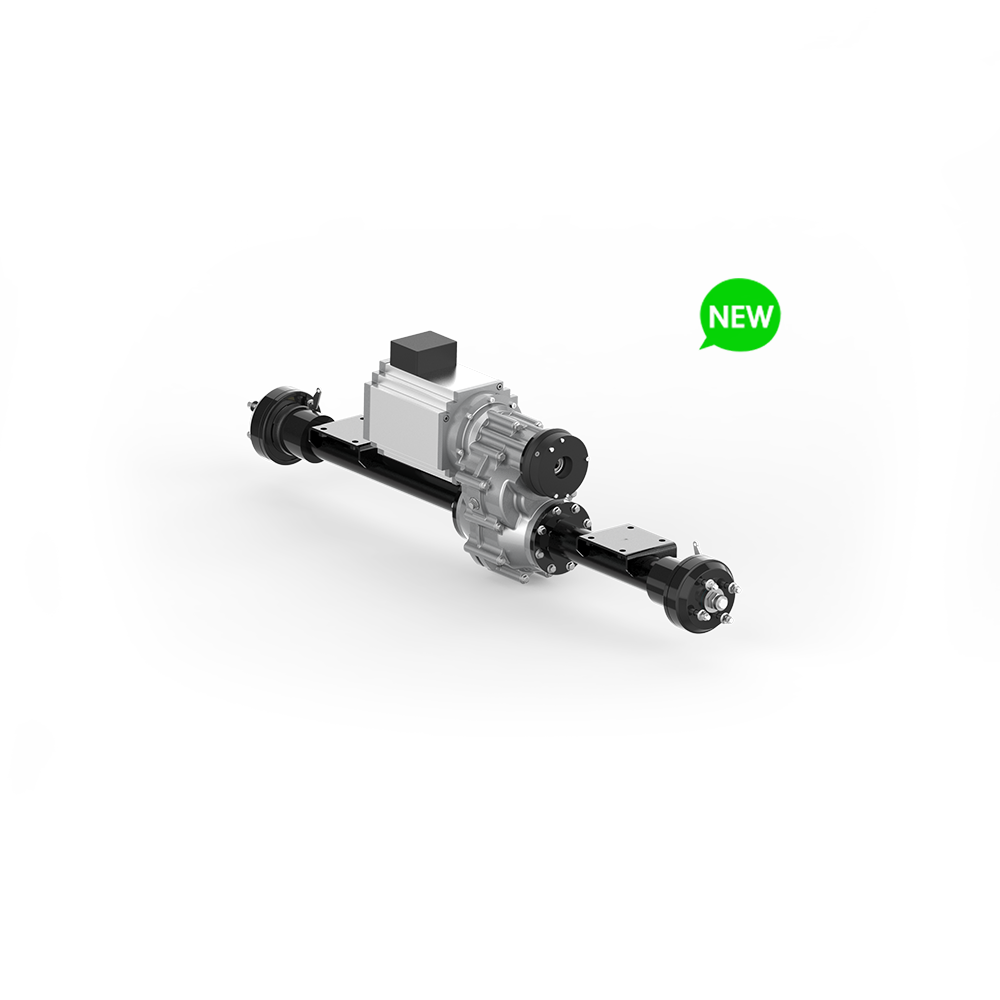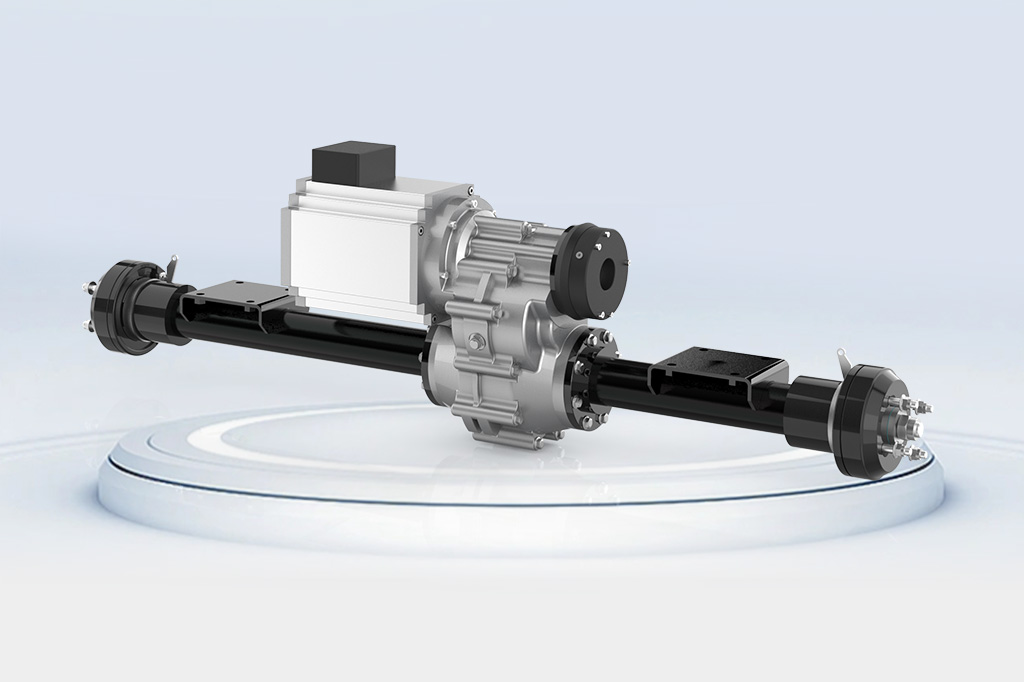
A transaxle works by regulating the power from a motor to the wheels using gearsets and differentials. The power range for this usually is from 150W watts to 20kw. With a small gear tolerance of 0.01 mm, the efficiency in achieving optimal speed or torque is maximized to provide the best driving smoothness while keeping energy loss as low as possible.
How gears affect noise reduction
The design and use of gears in the drive system directly affect noise performance. Gear operation inevitably generates noise, mainly due to friction between gears during contact and meshing. With appropriate material selections and accurate manufacturing processes, optimization in gear design can effectively reduce noise. Rotontek’s low-noise electric drive axle uses forged alloy steel gears that are finely ground, greatly reducing noise during gear meshing. This design can improve the efficiency of power transmission and greatly reduce noise levels, enhancing driving comfort. The power range of the drive axle, from 150 W to 20 kW, is used in various modern equipment. To this end, Rotontek strictly follows manufacturing standards and guarantees that the precision of every gear reaches micron levels, which directly improves the device’s noise reduction effect.

When the precision is improved to 0.02 millimeters or better, noise levels are reduced by 15% or more compared with traditional gear systems, making noise control more apparent. Of importance are the materials from which gears are made. Alloy steel, besides resisting wear and tear, reduces friction noise, keeping the gears quiet even in high-power applications. When changing gear material from traditional steel to high-strength alloy steel, the lifespan of the device increases by 20%, directly reducing the frequency of maintenance and replacement, thus saving costs. The shape and number of teeth of gears are also important parameters that affect noise reduction. Noise control can be further optimized by using helical gear designs. Compared with straight gears, helical gears can transmit power more smoothly and reduce noise by up to 30% during high-speed operation. Roton, through adjustments in gear shape, ensures that at 4,000 RPM, the device still maintains low noise levels, a design that is the top choice for noise-controlled products of many companies.
How power is transmitted
Power transmission mainly occurs through gears, drive shafts, and differentials. When the motor starts, 500 W–20 kW of power goes into the gear system and to the drive shaft, then evenly to the wheels via the differential. This process should guarantee a power transmission efficiency of over 95% to minimize energy loss. The transmission ratio of the gear set will directly affect the output speed of the power. If the gear transmission ratio is 3:1, then the speed triples, greatly improving vehicle speed and acceleration performance. In this respect, many industries design equipment to select the appropriate transmission ratio to achieve a balance between power output and energy consumption.

The differential also plays an important role in power transmission. It adjusts the distribution of power according to the difference in wheel speeds, so during turning, the wheels will not slip. This means that the differential design deviation should be less than or equal to 0.05 millimeters. Therefore, when making a sharp turn, vehicle stability improves by 20% in real driving situations. For such equipment, long-term steady operation is necessary, and the power transmission efficiency directly influences the service life of the equipment. Reducing the friction coefficient to 0.02 can lengthen the equipment’s service life by 30%, significantly saving maintenance costs. This technology is fully utilized in Roton’s electric drive axle, with its optimized gear transmission structure ensuring minimal power transmission loss.
How driving smoothness is achieved
Driving smoothness is closely related to stability in power transmission. Optimization in gear design and differential control can guarantee that power will not be suddenly interrupted during the transmission process from the motor to the wheels. The output power range between 500 W and 20 kW makes the equipment ideal for many scenarios where speed and precise power distribution are important. By maintaining the gear tolerance within 0.01 mm through precise gear meshing, the driving experience at 50 km/h can be improved by as much as 15%. This precise manufacturing process significantly reduces vibration levels during gear operation, which in turn provides a smoother ride for the driver.

Another determining factor is the design of the differential. The differential is capable of distributing power between the left and right wheels during turns, thus allowing the vehicle to avoid skidding or slipping. When the differential’s sensitivity reaches ±0.02 seconds, vehicle stability increases by 20%, especially during sharp turns or on slippery roads. The continuity of power output is closely related to driving smoothness. In most devices, the controller can control the motor’s power output very precisely, with a response time as quick as 0.5 seconds. In this way, there will be no interruption in power transmission. This technique helps guarantee continuous smooth acceleration and deceleration of the device under different speed conditions. The gear transmission ratio is an important factor that should be considered when designing for driving smoothness. A typical transmission ratio is 4:1, which will make power transmission smoother and suitable for scenarios that require high torque.



